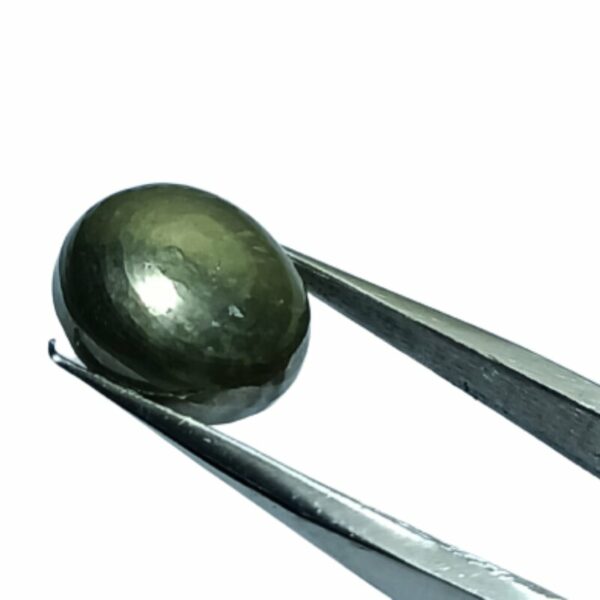
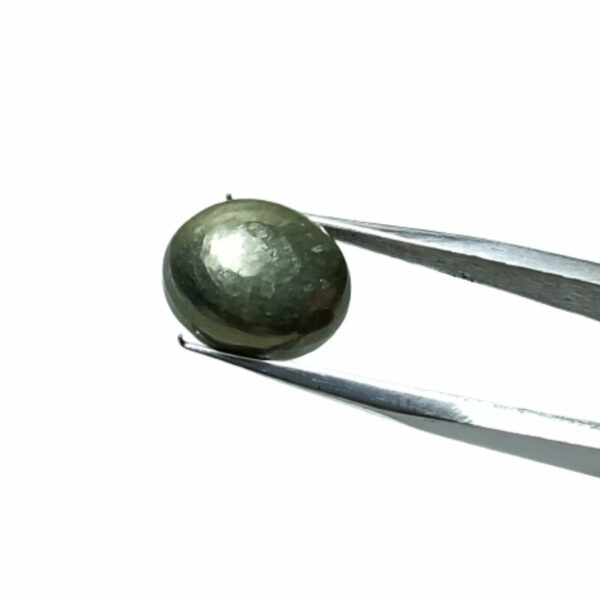
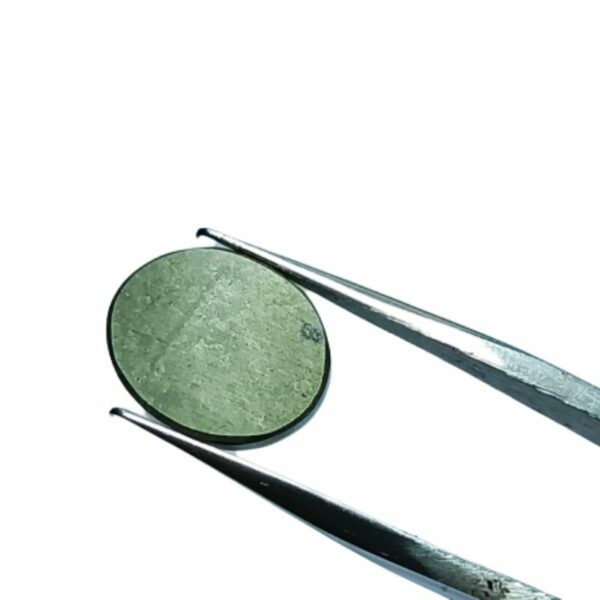
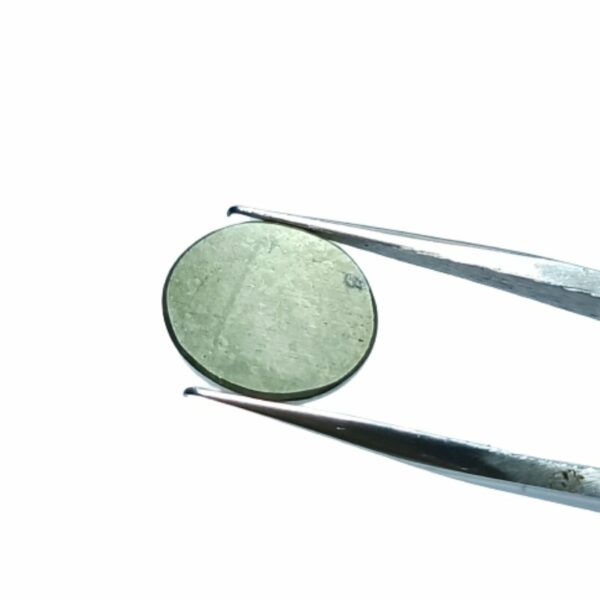
Mantrit (Energized) Authentic Golden Pyrite Stone With Lab Certified 7crt – 12crt
₹1,050.00 – ₹1,800.00 inc.GST
- Pyrite, also called “Fool’s Gold,” is known for its brassy yellow color and metallic luster.
- Pyrite has a cubic or pyritohedral crystal structure and often forms geometrically striking crystals.
- Historically, it has been confused with gold due to its appearance, leading to the nickname “Fool’s Gold.”
- Pyrite is found in various geological settings and is associated with spiritual beliefs of protection and abundance.
- Description
- Additional information
Description
NOTE: All images shown are for illustration purpose only. Actual product may vary.
Abhimantrit Authentic Golden Pyrite Stone With Lab Certified 7crt – 12crt
Pyrite, often known as “Fool’s Gold,” is a mineral with a fascinating history and unique characteristics. Here’s a description of pyrite:
Pyrite is a naturally occurring iron sulfide mineral known for its striking metallic luster and brassy yellow color. Its name is derived from the Greek word “pyr,” which means “fire,” due to its ability to produce sparks when struck against metal, resembling the action of flint and steel.
Key Features of Pyrite:
- Appearance: Pyrite crystals typically form in a cubic or pyritohedral (dodecahedral) shape, with a shiny, metallic surface that can appear gold-like, making it resemble actual gold. However, it has a distinct cubic or octahedral crystal structure.
- Mineral Composition: Pyrite is composed of iron (Fe) and sulfur (S), with a chemical formula FeS2. It is one of the most common sulfide minerals in the Earth’s crust.
- Historical Significance: Pyrite has a long history of being mistaken for gold, hence its nickname “Fool’s Gold.” Throughout the ages, prospectors and treasure hunters have been deceived by its appearance, thinking they had found valuable gold deposits.
- Industrial Uses: Pyrite has some industrial applications. It is used in the production of sulfur dioxide, a chemical used in various industrial processes, including the production of sulfuric acid. It has also been used in the past to produce iron sulfate for water purification.
- Metaphysical and Spiritual Beliefs: In some cultures and spiritual traditions, pyrite is believed to possess protective and grounding properties. It is associated with qualities like abundance, prosperity, and shielding against negative energies.
- Geological Occurrence: Pyrite is found in a variety of geological settings, including sedimentary rocks, hydrothermal veins, and as a component of metamorphic rocks. It can form as a primary mineral or as an accessory mineral in other rocks.
- Associated Minerals: Pyrite is often found in association with other minerals, such as quartz, calcite, and other sulfide minerals. These associations can lead to the formation of visually stunning mineral specimens.
- Crystallography: The crystal structure of pyrite is cubic, and it belongs to the Isometric crystal system. It often exhibits interesting geometric patterns and striations on its surface.
- Iron Pyrite vs. Marcasite: Pyrite is sometimes confused with marcasite, another iron sulfide mineral. While they have similar properties, marcasite has a different crystal structure and is more unstable and prone to oxidation.
In summary, pyrite is a captivating mineral known for its golden appearance, historical significance, and unique properties. While it may not be the coveted gold, it has its own allure and practical applications, along with metaphysical and spiritual associations in various cultures.
Additional information
| CARAT | 7 crt, 8 crt, 10 crt, 11 crt, 12 crt |
|---|